
- #Largest to smallest atomic radius code
- #Largest to smallest atomic radius series
- #Largest to smallest atomic radius free
(e) ionic radius Cs + (170) < atomic radius Cs (225) (d) ionic radius Rb + (149) < atomic radius Rb (211)

(c) ionic radius K + (138) < atomic radius K (196) (b) ionic radius Na + (102) < atomic radius Na (154) (a) ionic radius Li + (74) < atomic radius Li (134)
the cationic radius of an element is always less than its atomic radius?. We can wrote a chemical equation to represent this for any group 1 element (M) as shown below (A) Comparison of Atomic and Ionic Radius of Group 1 (IA, alkali metals) ElementsĪtoms of group 1 elements (M) lose 1 electron (e -) from their valence shell of electrons to form a cation with a charge of +1 (M +) Group 17 elements form anions with a charge of -1 Group 1 elements form cations with a charge of +1 Let's compare the radius of some elements' atoms with their respective ions. Down a Group of the Periodic Table from top to bottom, comparing ions with a similar charge, the ionic radius increases as the number of completed energy levels increases. Anions are larger than their respective atoms as electrons are added to the highest energy level (valence shell) the repulsion between the negatively charged electrons increases the ionic radius. Cations are smaller than their respective atoms as electrons are removed from the highest energy level (valence shell) while the positive nuclear charge remains the same thereby increasing the attraction between the remaining electrons and the nucleus resulting in a reduction in the size of the radius of the cation. Use the data given in the table below to find patterns (trends) in (B) Trends in the Atomic Radius of Elements in Period 3 atomic radius of the elements decreases from 134 pm to 69 pm across the period from left to rightĪtomic radius generally decreases across Period 2 from left to right as the nuclear charge increases. charge on the nucleus (nuclear charge) increases from +3 to +10 across the period from left to right. number of occupied energy levels (electron shells) remains the same (2 occupied electron shells) across the period. number of occupied energy levels (electron shells). Use the data in the table below for Group 1 elements to look for a pattern (or trend) in (A) Trends in the Atomic Radius of Group 1 (IA, Alkali Metals) Elements #Largest to smallest atomic radius free
No ads = no money for us = no free stuff for you! Trends in Atomic Radius in Groups of the Periodic TableĪs you go down a Group in the Periodic Table from top to bottom, the number of energy levels or electron shells increases so the atomic radius of the elements increases.Ĭompare the number of occupied energy levels (electron shells) and the radius of the atom of elements in Group 1 and in Group 17 as given in each section below: ionic radii of group 17 anions increases down the group.ionic radii of group 1 cations increases down the group.ionic radius of an anion is greater than atomic radius of the atom.ionic radius of a cation is less than atomic radius of the atom.is $52,000.Atomic radius decreases across a period from left to right Suppose that real GDP per capita in the U.S.A project has a level of systematic risk of 1.25.The marketing team at an internet music site wants a better.
#Largest to smallest atomic radius code
Write the VHDL code for a 4-bit register.
A 920-kg sports car collides into the rear end of a 2100-kg SUV. Need Java Code for this Algorithm Workbench Textbook Question:. These are persistent, debilitating and reduce. People with traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) commonly report. Which is NOT considered a way a business practicing Lean Assume that you are the newly appointed risk manager for a medical. Calculate the output of the network given the following neural. 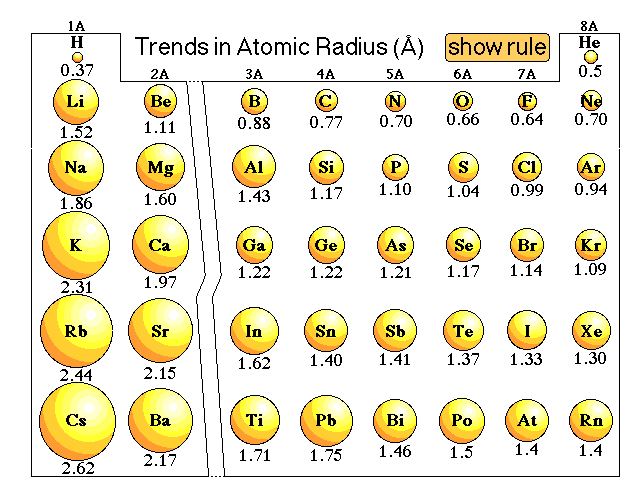
Greater than 0.10 to mean that there is no.
Evaluate the following regression results. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. Part C Arrange the following atoms in order of decreasing atomic radius Rank from largest to smallest. Part C Arrange the following atoms in order of decreasing atomic radius Rank from largest to smallest. #Largest to smallest atomic radius series
Arrange these elements in order of increasing first ionization energy, from sm Sb, Cl, Pb, P.Īrrange these elements in order of increasing first ionization energy, from sm Sb, Cl, Pb, P Largest radius Smallest radius Answer Bank c SnPb Ge
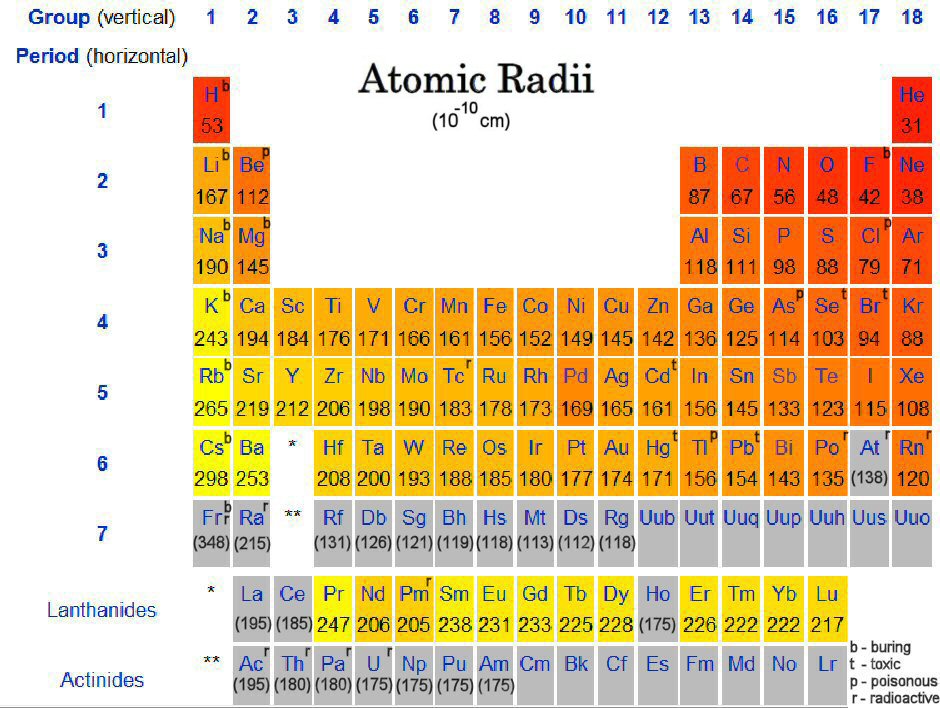
Largest radius Smallest radius Answer Bank c SnPb GeĪrrange these elements according to atomic radius.
Arrange these elements according to atomic radius.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
